Neocortex: Structure And Functions
Much of our evolutionary success is precisely due to the neocortex, or isocortex. This brain region has made possible such sophisticated processes as communication, writing, sociability, creativity or decision-making.
David Eagleman, writer and renowned neuroscientist at Stanford University, points out that every brain is unique, like a snowflake. No two are the same: our brains reflect the results of our experiences, behaviors and occupations. However, at the structural level, we are all the result of this unique phylogenetic development, where the neocortex is undoubtedly our greatest success as a species.
Composed of a large number of grooves, six layers and two millimeters thick, it contains about 30,000 million neurons. It is a neuronal layer that mainly covers the frontal lobes, the development and specialization of which is evident in primates and, of course, in humans. Knowing more information about this region of our brain will allow us to know ourselves better. Let’s deepen our thoughts on this below.
The neocortex, the most “new” and most extensive part of our brain
The neocortex is not very thick. However, it should be remembered that this structure is perfectly “folded” just below the skull. Hence the classic aspect of a brain full of furrows and convolutions. So if we could expand this whole area, it would be close to two meters in length.
- ?? In addition, the neocortex is also divided into two cerebral hemispheres, thus promoting greater neuronal specialization. It should also be noted that humans are the only mammal with such a high concentration of specialized neurons in so little space.
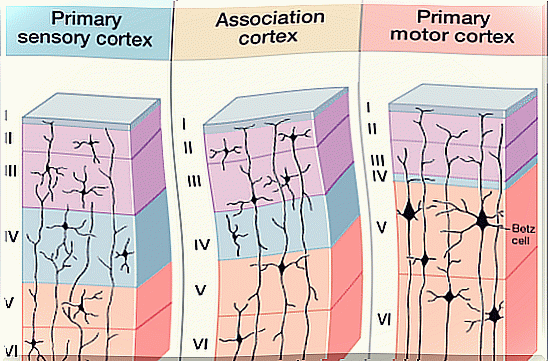
- ?? However, how the different layers of the neocortex are connected was until recently a mystery. As a study published in Frontiers in Psychology revealed , these layers establish themselves in the form of a “column”. That is, they conform, according to scientists, to laminar and columnar connectivity models .
- ?? The human neocortex also represents 76% of our gray matter.
- ?? It is interesting to know that this structure is not present in birds or in reptiles. However, scientists have found that many birds (such as crows) are incredibly intelligent despite lacking a defined neocortex.
What are the functions of the neocortex?
If we experience trauma to the neocortex, the consequences can be very serious. Thus, if you do not wear a helmet when you drive a motorcycle (or a bicycle) for example, you run the risk in the event of an accident of losing your ability to communicate, among other things. All of our cognitive processes, as well as our spatial intelligence, our ability to recognize faces or even access our self-awareness are embedded in this very distinctive space of humans and primates.
So let’s see what are its main functions.
Executive functions
As we pointed out earlier in this article, the neocortex is responsible for carrying out tasks such as problem solving, decision making, thinking, concentration, self-control, regulation of social behavior, etc. These are complex tasks that also respond to our learning capacity and the processes we have assimilated as a result of our evolution.
Language and writing
As we know, language is a human ability that puts us above all other species (It is true that some birds can also speak, but this is only an imitation and not a real one. communication skills).
On the other hand, the process of reading and writing also responds to a series of complex processes that occur in the neocortex. We are undoubtedly confronted here with a highly sophisticated capacity where we can associate written and oral symbols with meaning.
Sensory perception
Understanding and reacting to what we see and feel is another ability that the neocortex regulates and promotes.
Motor automation
What allows us to write, drive, play an instrument or even walk automatically without having to think about it? Although to perform all of these activities other neurological structures, such as the cerebellum, for example , come into play, it should be noted that all of these processes are made possible by the neocortex.
Learning and innovation skills
The ability to learn and transform what we learn – to create new things – is undoubtedly the highest and most distinctive process of being human. In other words, human beings do not limit themselves to imparting information, to acquiring new skills. We are also able to transform reality and increase our knowledge. This is enabled through observation, analysis, reflection, trial and error, and innovation.
This ability to learn and create has also allowed us to grow as a species. Likewise, the evolution of the neocortex arose from our social interactions. In addition, we know that the size of this structure is directly linked to the number of individuals forming a social group.
Therefore, we cannot leave out an even more interesting aspect: we continue to evolve. In addition, it was in 1999 that neuroscientists discovered the great neuroplasticity of the neocortex. That is to say that the human being continues to create neural connections throughout his life. Our experience and behavior can promote the creation of a stronger neocortex. More skillful. And more resistant over time.